BES

Product Description
BES, or N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a widely used buffer in biochemistry and molecular biology research.
Product:
BES
CAS:
10191-18-1
Synonym:
N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid; N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)taurine
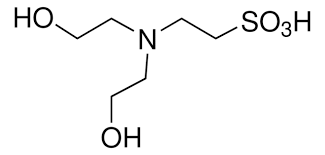
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystalline powder
Density
1.210 g/cm3
Melting point
150-155 °C
Molecular Weight
213.25
Purity
≥99%
Refractive index
1.5500
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote



BES used in many
industry applications
BES, or N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a chemical compound with various industrial applications. Here are some of its uses:
- Biological Buffer: BES is commonly used as a buffering agent in biological and biochemical research to maintain the pH of solutions within a specific range. It is particularly useful in cell culture, enzyme assays, and protein purification.
- Electrophoresis: It serves as a buffer component in gel electrophoresis techniques such as polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and agarose gel electrophoresis. BES helps to stabilize the pH of the running buffer and maintain the integrity of nucleic acids and proteins during electrophoresis.
- Protein Crystallization: BES is used as a crystallization buffer in protein crystallography experiments. It provides a stable pH environment for protein crystallization and can influence the size, morphology, and quality of protein crystals.
- Enzyme Kinetics: It is employed in enzymology studies to investigate enzyme kinetics and substrate specificity. BES buffers are often used to maintain constant pH conditions in enzyme assays, allowing researchers to accurately measure enzyme activity.
- Diagnostic Assays: BES is utilized in various diagnostic assays and immunoassays for detecting biomolecules such as antibodies, antigens, and nucleic acids. It helps stabilize the pH of assay buffers and ensures accurate and reproducible results.
- Medicinal Chemistry: BES may serve as a starting material or reagent in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds and drug formulations. Its chemical properties make it suitable for use in medicinal chemistry research and drug discovery.
- Photography: It finds applications in photography as a component of developer solutions and fixing baths. BES buffers are used to control the pH of photographic processing solutions and optimize the development process.
- Industrial Processes: BES may be employed in various industrial processes where precise pH control is required, such as in the production of chemicals, polymers, and specialty materials.