CHES

Product Description
CHES (2-(Cyclohexylamino)ethanesulfonic acid) is a buffering agent commonly used in biochemical and biological research.
Product:
CHES
CAS:
103-47-9
Synonym:
2-(Cyclohexylamino)ethanesulfonic acid; N-Cyclohexyltaurine
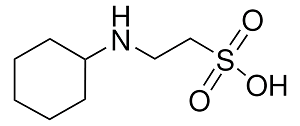
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystalline powder
Density
1.2045 g/cm3
Melting point
320 °C
Molecular Weight
207.29
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥99.5%
Refractive index
1.4903
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote



CHES used in many
industry applications
CHES (2-(Cyclohexylamino)ethanesulfonic acid) is a buffering agent commonly used in biochemical and biological research. Here are some of its main uses:
- Buffer Solution: CHES is widely employed as a buffering agent in various biochemical and biotechnological applications. It helps maintain a stable pH environment, particularly in the physiological range (pH 8.6–10.0), making it suitable for buffering biological samples, cell culture media, protein solutions, and enzyme reactions. CHES buffer is often utilized in electrophoresis, chromatography, enzyme assays, and nucleic acid hybridization experiments where precise pH control is essential for optimal performance and reproducible results.
- Protein Crystallization: CHES is utilized in protein crystallography as a crystallization buffer for the growth of protein crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis. Its low UV absorbance and minimal interference with protein structures make it a preferred choice for crystallization trials. CHES buffer provides stable and reproducible conditions for protein crystallization, facilitating the determination of protein structures and the elucidation of biological functions through structural biology techniques.
- Membrane Protein Studies: CHES buffer is often employed in the solubilization and characterization of membrane proteins, which are integral components of cell membranes and play critical roles in cellular signaling, transport, and homeostasis. Its mild nature and compatibility with lipid bilayers make it suitable for maintaining the stability and activity of membrane proteins during purification, reconstitution, and functional assays. CHES buffer is frequently used in studies involving ion channels, receptors, transporters, and other membrane-bound proteins.
- Enzyme Kinetics: CHES buffer is utilized in enzyme kinetics studies to investigate the catalytic activity, substrate specificity, and inhibition mechanisms of enzymes. Its pH stability and minimal chelating properties ensure accurate measurements of enzyme kinetics parameters, such as Michaelis-Menten constants (KM) and maximal reaction rates (Vmax). CHES buffer is compatible with a wide range of enzymes, including oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases, enabling researchers to elucidate enzyme function and regulation in biochemical pathways.
- Cell Culture: CHES buffer is sometimes used in cell culture media formulations to maintain physiological pH conditions for the growth and maintenance of mammalian cells in vitro. Its compatibility with cell culture systems and minimal cytotoxicity make it suitable for supporting cell viability, proliferation, and metabolic activities. CHES-buffered media are employed in cell-based assays, drug screening studies, and recombinant protein expression systems where consistent pH control is essential for reproducible experimental outcomes.
- DNA and RNA Electrophoresis: CHES buffer is utilized in nucleic acid electrophoresis techniques, such as agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), for the separation and analysis of DNA and RNA molecules based on their size and charge. Its buffering capacity and compatibility with nucleic acid samples ensure sharp and well-resolved bands during electrophoretic migration. CHES buffer is commonly used in molecular biology laboratories for DNA sequencing, PCR product analysis, restriction enzyme digests, and Northern/Southern blotting experiments.
- Diagnostic Assays: CHES buffer is employed in diagnostic assays and immunoassay techniques for the detection and quantification of biomolecules, including proteins, antibodies, antigens, and nucleic acids. Its stable pH conditions and minimal interference with assay components ensure accurate and reliable results in diagnostic applications such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and nucleic acid hybridization assays. CHES-buffered solutions provide consistent assay performance and reproducible analytical measurements in clinical diagnostics and research laboratories.