HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Methyl Formate

Product Description
Methyl formate is a chemical compound with various industrial applications.
Product:
Methyl Formate
CAS:
107-31-3
Synonym:
Methyl methanoate; Formic acid methyl ester
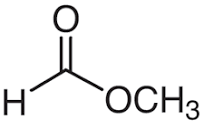
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Boiling point
31.5 °C
Density
0.98 g/cm3
Flash Point
-27 °C
Melting point
-100 °C
Molecular Weight
60.05
Odor
Pleasant, ethereal odor
Purity
99%
Refractive index
1.344
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Methyl Formate
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Methyl Formate used in many
industry applications
Methyl formate is a chemical compound with various industrial applications. Here are some of its uses:
- Solvent: Methyl formate is used as a solvent in various industrial processes, including the production of paints, coatings, adhesives, and cleaning products. It can dissolve a wide range of organic compounds.
- Chemical Intermediate: It serves as an intermediate in organic synthesis for the production of various chemicals, including formic acid, formamide, and methyl acetate.
- Fumigant: Methyl formate is used as a fumigant for pest control in agricultural products, stored grains, and timber. It has insecticidal properties and can penetrate materials to eradicate pests.
- Refrigerant: It has been used as a refrigerant in some applications due to its low boiling point and good heat transfer properties. However, its use has declined due to environmental concerns.
- Foaming Agent: Methyl formate is used as a blowing agent in the production of foam materials, such as polyurethane foams and polystyrene foams, to generate gas bubbles and impart cellular structure.
- Chemical Synthesis: It is employed in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals, where it serves as a methylating agent or a precursor to other compounds.
- Carbon Source: Methyl formate can be used as a carbon source in microbial fermentation processes for the production of various chemicals, biofuels, and biopolymers.