HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Diisopropyl Ether

Product Description
Diisopropyl ether is a chemical compound with various industrial applications.
Product:
Diisopropyl Ether
CAS:
108-20-3
Synonym:
Isopropyl ether; 2-Isopropoxypropane
Structure:
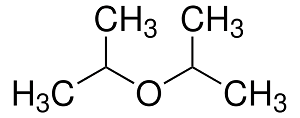
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Boiling point
68-69 °C
Density
0.725 g/cm3
Flash Point
-28 °C
Melting point
−85 °C
Molecular Weight
102.17
Odor
Sharp, sweet, ether-like odor
Purity
≥98.5%
Refractive index
1.367
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Diisopropyl Ether
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Diisopropyl Ether used in many
industry applications
Diisopropyl ether is a chemical compound with various industrial applications. Here are some of its main uses:
- Solvent: Diisopropyl ether is commonly used as a solvent in various industrial processes, including pharmaceuticals, coatings, and chemical synthesis. Its low boiling point and good solubility properties make it suitable for dissolving a wide range of organic compounds.
- Extraction Agent: It is employed as an extraction agent in the purification of natural products, such as essential oils and flavors. Diisopropyl ether can selectively extract target compounds from complex mixtures, facilitating the isolation and concentration of desired components.
- Reagent: In organic synthesis, diisopropyl ether is utilized as a reaction medium or reagent in various reactions, such as Grignard reactions, Williamson ether synthesis, and organometallic reactions. It can serve as a mild Lewis base or Lewis acid scavenger, enabling the formation of desired products with high yields and purity.
- Liquid Chromatography: Diisopropyl ether is used as a mobile phase solvent in liquid chromatography techniques, particularly in gas chromatography (GC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Its relatively low viscosity and volatility make it suitable for chromatographic separations, allowing for the analysis and quantification of organic compounds in complex mixtures.
- Aerosol Propellant: It finds application as a propellant in aerosol formulations, such as spray paints, adhesives, and insecticides. Diisopropyl ether's low boiling point and volatility allow it to vaporize quickly upon release from the aerosol container, generating the pressure necessary to propel the product out of the canister.
- Cosmetic and Personal Care Products: Diisopropyl ether is sometimes used as a solvent or carrier in cosmetic and personal care products, including perfumes, hair sprays, and skin lotions. It can help dissolve and disperse active ingredients, enhancing the formulation's stability and sensory properties.
- Chemical Intermediate: It serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and specialty chemicals. Diisopropyl ether can undergo various functional group transformations, including oxidation, reduction, and alkylation, to yield valuable intermediates for further chemical elaboration.
- Lubricant Additive: In some industrial lubricants and cutting fluids, diisopropyl ether is used as an additive to improve lubricity and reduce friction between moving parts. It can enhance the performance of lubricants by reducing wear, extending equipment life, and improving energy efficiency.