HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Dibutylamine

Product Description
Dibutylamine, a chemical compound with various industrial applications, serves several roles due to its unique properties.
Product:
Dibutylamine
CAS:
111-92-2
Synonym:
N-Butyl-1-butanamine; N,N-Dibutylamine
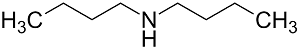
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Yellow-colored liquid
Boiling point
159 °C
Density
0.767 g/cm3
Flash Point
57 °C
Melting point
−62 °C
Molecular Weight
129.24
Odor
Amine-like odor
Purity
≥99.5%
Refractive index
1.417
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Dibutylamine
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Dibutylamine used in many
industry applications
Dibutylamine, a chemical compound with various industrial applications, serves several roles due to its unique properties. Here are some of its primary uses:
- Intermediate: Dibutylamine serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of numerous organic compounds, including agricultural chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemicals. It undergoes various reactions such as alkylation, condensation, and hydrogenation to produce valuable intermediates used in diverse industrial processes.
- Corrosion Inhibitor: It finds application as a corrosion inhibitor in metalworking fluids, such as cutting fluids and lubricants, to protect metal surfaces from corrosion and rusting. Dibutylamine forms a protective film on metal surfaces, reducing friction and wear during machining operations while enhancing the longevity of metalworking tools and components.
- Surfactant: Dibutylamine can be employed as a surfactant or wetting agent in various formulations, such as detergents, emulsifiers, and foaming agents. It helps reduce surface tension, improve wetting and dispersion of substances, and stabilize emulsions, leading to enhanced cleaning, dispersion, and foaming properties in industrial and household products.
- Flotation Agent: In the mining industry, dibutylamine is utilized as a flotation agent in the separation of minerals from ores during the flotation process. It selectively binds to mineral surfaces, facilitating the separation of valuable minerals from gangue materials based on their hydrophobic or hydrophilic properties, thereby improving the efficiency of mineral processing operations.
- Corrosion Inhibitor: Dibutylamine is sometimes used as a corrosion inhibitor in cooling water treatment formulations, particularly in industrial cooling systems and heat exchangers. It helps prevent the formation of scale, corrosion, and fouling on metal surfaces by forming a protective layer and inhibiting the oxidation of metals exposed to circulating water.
- Solvent: It serves as a solvent or solvent additive in various industrial processes, such as chemical synthesis, extraction, and purification. Dibutylamine is compatible with a wide range of organic solvents and can be used as a reaction medium or extraction solvent in the production of specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals.
- Organic Synthesis: Dibutylamine is utilized in organic synthesis as a versatile building block for the preparation of nitrogen-containing compounds, such as amines, amides, and quaternary ammonium salts. It participates in numerous synthetic transformations, including nucleophilic substitution, reductive amination, and condensation reactions, enabling the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
- Chemical Intermediates: It serves as a starting material for the synthesis of various chemical intermediates used in the production of rubber chemicals, textile auxiliaries, plasticizers, and specialty additives. Dibutylamine undergoes reactions such as alkylation, acylation, and halogenation to yield functionalized compounds with specific chemical and physical properties.
- Herbicide Additive: In agriculture, dibutylamine may be used as an additive or co-formulant in herbicide formulations to enhance the performance and efficacy of herbicidal active ingredients. It aids in the dispersion, solubilization, and uptake of herbicides by target plants, improving weed control and reducing the risk of off-target drift or environmental contamination.
- Pharmaceuticals: Dibutylamine finds application in pharmaceutical synthesis as a reagent or auxiliary agent in the production of pharmaceutical intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). It can be utilized in medicinal chemistry and drug discovery processes to introduce specific functional groups or molecular motifs into drug molecules, enabling the development of new therapeutic agents.