MOPS

Product Description
MOPS, or 3-(N-Morpholino)propanesulfonic acid, is a common buffer used in various biochemical and molecular biology applications.
Product:
MOPS
CAS:
1132-61-2
Synonym:
3-(N-Morpholino)propanesulfonic acid; 4-Morpholinepropanesulfonic acid
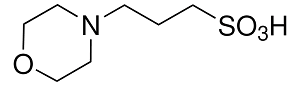
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystalline powder
Density
1.3168 g/cm3
Melting point
277-282 °C
Molecular Weight
209.26
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥99.5%
Refractive index
1.6370
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote



MOPS used in many
industry applications
MOPS, or 3-(N-Morpholino)propanesulfonic acid, is a common buffer used in various biochemical and molecular biology applications. Here are some of its key industrial uses:
- Buffer Solution: MOPS is extensively utilized as a buffering agent in laboratory experiments, particularly in molecular biology, biochemistry, and protein research. It helps maintain a stable pH environment, ensuring accurate and reproducible results in enzymatic assays, protein electrophoresis, and nucleic acid analysis.
- Cell Culture: MOPS is added to cell culture media to regulate pH and provide a suitable chemical environment for cell growth and viability. It helps maintain physiological conditions optimal for cell proliferation, differentiation, and metabolic activity in vitro.
- Protein Purification: In protein purification processes, MOPS buffers are used during chromatography and protein isolation steps to control pH gradients and stabilize protein structures. They facilitate the efficient separation and purification of target proteins from complex biological samples.
- RNA Analysis: MOPS buffers are employed in RNA analysis techniques, such as RNA gel electrophoresis and Northern blotting. They help ensure the integrity and stability of RNA molecules during sample preparation, electrophoretic separation, and transfer onto membranes for hybridization.
- Enzyme Kinetics: MOPS buffers are commonly used in enzymatic assays to study enzyme kinetics and biochemical reactions. Their precise pH control and low ionic strength minimize interference with enzyme activity, allowing researchers to accurately measure reaction rates and substrate turnover.
- Biotechnology: MOPS buffers play a crucial role in various biotechnological processes, including recombinant protein expression, DNA sequencing, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). They help optimize reaction conditions, enhance enzyme performance, and improve the reproducibility of experimental results.
- Diagnostic Assays: MOPS buffers are utilized in diagnostic assays and medical testing procedures to maintain pH stability and minimize non-specific binding interactions. They contribute to the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic tests for detecting biomarkers, pathogens, and disease-related molecules.
- Drug Formulation: In pharmaceutical research and drug formulation, MOPS buffers may be incorporated into formulations to adjust pH, solubility, and stability of drug compounds. They assist in the development of drug delivery systems and formulations with optimal bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.