HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde

Product Description
P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde, also known as 4-n-Propylbenzaldehyde, is an aromatic aldehyde with various industrial applications.
Product:
P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde
CAS:
28785-06-0
Synonym:
4-Propylbenzaldehyde; Benzaldehyde, 4-propyl-
Structure:
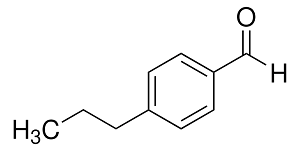
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless to yellow liquid
Boiling point
240 °C
Density
1.0050 g/cm3
Melting point
19 °C
Molecular Weight
148.20
Odor
Faint aromatic odor
Purity
95%
Refractive index
1.532
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde used in many
industry applications
P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde, also known as 4-n-Propylbenzaldehyde, is an aromatic aldehyde with various industrial applications. Here are some of its uses:
- Fragrance Industry: P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of fragrances. Its aromatic properties contribute to the creation of various perfumes and scents.
- Flavor Industry: It is used in the production of flavoring agents, providing a distinctive aroma that enhances the taste profiles of food and beverages.
- Pharmaceuticals: This compound serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds. It is used in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other medicinal products.
- Agrochemicals: P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde is used in the synthesis of agrochemical products, such as pesticides and herbicides, contributing to their efficacy in agricultural applications.
- Dyes and Pigments: It is utilized as an intermediate in the production of dyes and pigments, helping to achieve desired colors and properties in textiles and other materials.
- Resins and Polymers: This compound is used in the synthesis of resins and polymers, providing specific chemical properties that enhance the performance and durability of these materials.
- Chemical Research: P-N-Propylbenzaldehyde is used in various chemical research applications, including the development of new synthetic methods and the study of reaction mechanisms.
- Organic Synthesis: It serves as a building block in organic synthesis, enabling the creation of more complex chemical structures for various industrial and research purposes.