Glycidoxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane

Product Description
Glycidoxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane, also known as GPTS, is a silane coupling agent with various industrial applications.
Product:
Glycidoxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane
CAS:
2897-60-1
Synonym:
Diethoxy(3-glycidyloxypropyl)methylsilane; 3-(Methyldiethoxysilyl)propyl glycidyl ether
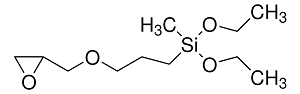
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Boiling point
122-126 °C/5 mmHg
Density
0.978 g/cm3
Flash Point
>110 °C
Molecular Weight
248.39
Purity
97%
Refractive index
1.431
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Glycidoxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Glycidoxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane used in many
industry applications
Glycidoxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane, also known as GPTS, is a silane coupling agent with various industrial applications. Here are some of its common uses:
- Adhesion Promoter: GPTS is widely used as an adhesion promoter in coatings, adhesives, and sealants. It enhances the adhesion between organic substrates and inorganic surfaces, such as metals, glass, ceramics, and minerals, by forming strong chemical bonds.
- Surface Modifier: It serves as a surface modifier for fillers, pigments, and reinforcing materials in composite materials and polymer formulations. GPTS-treated surfaces exhibit improved wetting, dispersibility, and compatibility with resin matrices, leading to enhanced mechanical properties and durability.
- Crosslinking Agent: In polymer chemistry, GPTS functions as a crosslinking agent or coupling agent for thermosetting resins, such as epoxy, phenolic, and melamine resins. It reacts with functional groups in the resin matrix to form covalent bonds, resulting in improved strength, stiffness, and heat resistance.
- Surface Treatment: GPTS is employed as a surface treatment agent for various substrates, including metals, glass fibers, and mineral fillers. It modifies the surface energy and chemistry of substrates, leading to enhanced wetting, bonding, and compatibility with organic matrices in composite materials.
- Adhesive Formulations: It is utilized in the formulation of epoxy adhesives and sealants to improve adhesion to difficult-to-bond substrates, such as metals, plastics, and ceramics. GPTS-functionalized adhesives exhibit superior bond strength, chemical resistance, and moisture resistance.
- Coatings and Paints: GPTS is incorporated into coatings and paint formulations as a crosslinking agent, adhesion promoter, or surface modifier. It improves the adhesion, durability, and corrosion resistance of coatings on metal surfaces, concrete, and other substrates.
- Composites Manufacturing: GPTS plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics (FRP), carbon fiber composites, and polymer matrix composites (PMC). It enhances the interfacial adhesion between fibers and resin matrices, resulting in composite materials with improved mechanical properties and dimensional stability.
- Concrete Admixtures: In the construction industry, GPTS is used as a concrete admixture to improve the bonding between concrete and reinforcing materials, such as steel rebars and glass fibers. It enhances the strength, durability, and chemical resistance of concrete structures.