Tricine

Product Description
Tricine, also known as N-[Tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl]glycine, is a zwitterionic buffer commonly used in biochemical and molecular biology applications.
Product:
Tricine
CAS:
5704-04-1
Synonym:
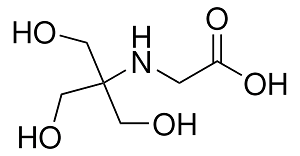
N-[Tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl]glycine
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystals
Density
1.05 g/cm3
Melting point
187 °C
Molecular Weight
179.17
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥99%
Refractive index
1.4240
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote



Tricine used in many
industry applications
Tricine, also known as N-[Tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl]glycine, is a zwitterionic buffer commonly used in biochemical and molecular biology applications. Here are some of its industrial uses:
- Electrophoresis: Tricine is frequently employed as a buffering agent in electrophoresis techniques, such as SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). It helps maintain a stable pH environment, allowing proteins to migrate through the gel matrix efficiently.
- Protein Purification: Tricine is used in protein purification methods, such as chromatography, to maintain a constant pH during the separation and elution steps. It aids in preserving the stability and activity of the target proteins.
- Cell Culture: Tricine is sometimes included in cell culture media formulations to control the pH and provide a stable environment for cell growth and maintenance. It helps prevent fluctuations in pH that could affect cellular processes.
- Enzyme Kinetics: Tricine is utilized in enzymatic assays and kinetic studies to maintain a consistent pH, which is crucial for accurate measurement of enzyme activity and substrate turnover rates.
- Buffer Solutions: Tricine is a component of buffer solutions used in various biochemical assays, immunoassays, and diagnostic kits. Its buffering capacity and compatibility with a wide range of biological samples make it suitable for diverse applications in the life sciences.
- Protein Crystallization: Tricine is sometimes employed in protein crystallization experiments as a buffer component to maintain the stability and solubility of proteins under crystallization conditions. It helps optimize the pH for the formation of high-quality protein crystals suitable for X-ray crystallography.