HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Dimer Acid

Product Description
Dimer Acid, a dimerized fatty acid, is used in the production of resins and other industrial applications, offering properties like flexibility and toughness.
Product:
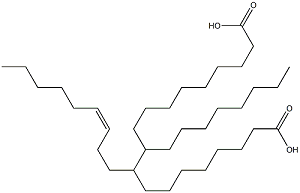
Dimer Acid
CAS:
61788-89-4
Synonym:
Dimerised Fatty Acid; Dimerized Fatty Acid; Dimer Fatty Acid
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Viscous liquid
Boiling point
300-350
Color
Light yellow
Density
0.92-0.94
Flash Point
>230
Melting point
-65 to -45
Molecular Weight
564.92
Odor
Mild
Purity
95
Refractive index
1.45-1.47
Solubility
Insoluble in water
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote


