HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Saccharin

Product Description
Saccharin, a synthetic sweetener, is notable for its non-caloric property and is extensively used in various applications due to its intense sweetness.
Product:
Saccharin
CAS:
81-07-2
Synonym:
2,3-Dihydroxy-1,2-benzisothiazol-3-one-1,1-dioxide; 2-Sulfobenzoic acid imide; o-Benzoic sulfimide
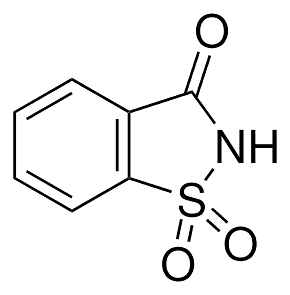
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystalline powder
Density
0.828 g/cm3
Melting point
226-229 °C
Molecular Weight
183.18
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥99%
Refractive index
1.5500
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote



Saccharin used in many
industry applications
Saccharin, a synthetic sweetener, is notable for its non-caloric property and is extensively used in various applications due to its intense sweetness. Here are some key industrial applications:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Saccharin is widely used as a sugar substitute in soft drinks, candies, cookies, and chewing gums due to its zero-calorie content, benefiting people with diabetes or those monitoring calorie intake.
- Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceuticals, saccharin is used to sweeten medications, particularly liquid medicines, chewable tablets, and pills, making them palatable without increasing blood sugar levels.
- Personal Care Products: It finds application in personal care products such as toothpaste and mouthwashes as a sweetener to improve taste without promoting tooth decay.
- Dietary Products: Saccharin is used in the production of dietary foods and beverages, offering a sweet taste without the calories associated with sugar, catering to weight-conscious consumers.
- Industrial Applications: Beyond consumables, saccharin is utilized in certain industrial processes as an additive to electroplating baths to improve the brightness and smoothness of plated metals.