Choline Bitartrate

Product Description
Choline Bitartrate, a form of choline, serves as an essential nutrient involved in various physiological processes. It is particularly significant for its role in brain health, liver function, and muscle movement.
Product:
Choline Bitartrate
CAS:
87-67-2
Synonym:
2-(Hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium bitartrate; Choline tartrate
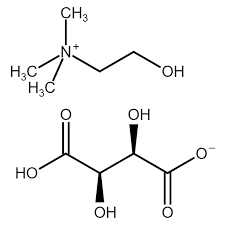
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystalline powder
Boiling point
399.3 °C
Density
1.47 g/cm3
Flash Point
209.4 °C
Melting point
149-153 °C
Molecular Weight
253.25
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥98%
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Choline Bitartrate
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Choline Bitartrate used in many
industry applications
Choline Bitartrate, a form of choline, serves as an essential nutrient involved in various physiological processes. It is particularly significant for its role in brain health, liver function, and muscle movement. Here are some of its notable applications:
- Dietary Supplements: Widely used in dietary supplements to support cognitive function, memory enhancement, and overall brain health.
- Nutritional Fortification: Incorporated into health foods and beverages to ensure adequate intake of choline, which is crucial for maintaining cellular membrane structure and function.
- Memory and Cognitive Support: Research suggests that choline bitartrate supplements may benefit cognitive function, making it a popular choice for improving memory and brain performance.
- Liver Health: Used to prevent and treat liver diseases such as fatty liver disease, owing to choline's role in fat metabolism and transport.
- Prenatal Nutrition: Essential for pregnant women, as adequate choline intake is critical for fetal brain development and may reduce the risk of neural tube defects.
- Athletic Performance: Some studies indicate that choline bitartrate might improve endurance and reduce fatigue in athletes by enhancing acetylcholine synthesis, a neurotransmitter involved in muscle contraction.
- Mood Regulation: It is explored for its potential role in mood regulation and may have implications for treating disorders like depression.