Gelatin

Product Description
Gelatin is a protein derived from collagen, a natural animal protein found in the connective tissues, bones, and skin of animals. It has a wide range of industrial applications due to its unique properties.
Product:
Gelatin
CAS:
9000-70-8
Synonym:
Gelfoam; Collagens, gelatins
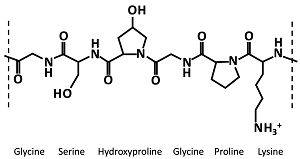
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless or slightly yellow transparent solid
Density
1.2 g/cm3
Melting point
>226 °C
Molecular Weight
477.55
Odor
Odorless
Purity
99%
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote



Gelatin used in many
industry applications
Gelatin is a protein derived from collagen, a natural animal protein found in the connective tissues, bones, and skin of animals. It has a wide range of industrial applications due to its unique properties such as gelling, thickening, stabilizing, and binding. Some of the key industrial uses of gelatin include:
- Food and Beverage: Gelatin is widely used in the food industry as a gelling agent, stabilizer, thickener, and texturizer in various food products. It is commonly found in confectionery items like gummy candies, marshmallows, and gelatin desserts (e.g., Jell-O). Gelatin is also used in dairy products, yogurt, ice cream, soups, sauces, and meat products to improve texture, mouthfeel, and stability.
- Pharmaceuticals: Gelatin is utilized in the pharmaceutical industry to produce capsules, softgels, and tablets for oral drug delivery. Gelatin capsules are preferred for encapsulating liquid, semi-solid, or dry drug formulations due to their ease of swallowing, biocompatibility, and dissolution properties. Gelatin is also used as a suspending agent, coating agent, or binder in pharmaceutical formulations to improve drug stability and bioavailability.
- Photography: Gelatin is an essential component of photographic emulsions used in traditional film photography. Gelatin acts as a binder and support matrix for light-sensitive silver halide crystals dispersed in photographic films and papers. During the development process, gelatin facilitates the formation of the latent image and the subsequent development of the visible image.
- Cosmetics: Gelatin is incorporated into cosmetic formulations such as skincare products, hair care products, and makeup items due to its film-forming, moisturizing, and thickening properties. It is used in creams, lotions, shampoos, conditioners, mascaras, and nail polishes to enhance texture, stability, and performance.
- Medical and Healthcare: Gelatin-based products are used in medical and healthcare applications such as wound dressings, hemostatic sponges, surgical adhesives, and tissue engineering scaffolds. Gelatin biomaterials provide a biocompatible and biodegradable matrix for wound healing, tissue repair, and regenerative medicine applications.
- Art and Crafts: Gelatin is utilized in art and craft projects as a mold-making material, casting agent, and adhesive. It is commonly used in sculpture, modeling, prop-making, and mixed media artwork to create three-dimensional objects, decorations, and embellishments.