HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Quinoline

Product Description
Quinoline, a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, plays a critical role in various industrial applications due to its unique chemical properties.
Product:
Quinoline
CAS:
91-22-5
Synonym:
1-Benzazine; 2,3-Benzopyridine
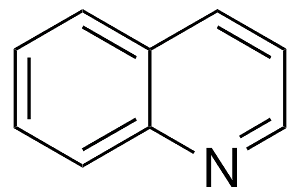
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Boiling point
237 °C
Density
1.093 g/cm3
Flash Point
105 °C
Melting point
-15 °C
Molecular Weight
129.16
Odor
Unpleasant odor
Purity
98%
Refractive index
1.625
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote



Quinoline used in many
industry applications
Quinoline, a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, plays a critical role in various industrial applications due to its unique chemical properties. Below are some of the notable uses of quinoline:
- Pharmaceuticals Production: Quinoline is a key starting material in the synthesis of antimalarial drugs, such as chloroquine and quinine, along with other pharmaceutical compounds.
- Agricultural Chemicals: It serves as a precursor in the manufacture of herbicides, fungicides, and plant growth regulators, contributing to the agricultural industry's chemical arsenal.
- Chemical Synthesis: Quinoline is used in organic synthesis, providing a foundational structure for the production of dyes, rubber chemicals, and flavoring agents.
- Corrosion Inhibitor: In the oil and gas industry, quinoline derivatives are employed as corrosion inhibitors to protect metal surfaces in acidic environments.
- Solvent: Due to its solvent properties, quinoline is used in the extraction and purification of various organic compounds.
- Antiseptic Formulations: Some quinoline derivatives have antiseptic properties, making them suitable for use in certain medical and cleaning products.
- Research and Development: In academic and industrial research, quinoline and its derivatives are studied for their potential applications in new materials, electronics, and advanced pharmaceuticals.