HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Dibenzylamine

Product Description
Dibenzylamine is a chemical compound with various industrial applications.
Product:
Dibenzylamine
CAS:
103-49-1
Synonym:
N-benzyl-1-phenylmethanamine; N-Benzylbenzylamine
Structure:
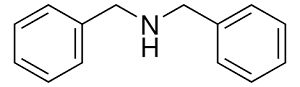
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Boiling point
300 °C
Density
1.026 g/cm3
Melting point
−26 °C
Molecular Weight
197.28
Odor
Weak odor
Purity
97%
Refractive index
1.574
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote
We Offer Dibenzylamine
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Dibenzylamine used in many
industry applications
Dibenzylamine is a chemical compound with various industrial applications. Here are some of its primary uses:
- Intermediates Synthesis: Dibenzylamine serves as a valuable intermediate in organic synthesis, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. It undergoes various reactions such as alkylation, acylation, and condensation to form complex organic compounds with diverse functionalities.
- Corrosion Inhibitors: Dibenzylamine is employed as a corrosion inhibitor in metalworking fluids, lubricants, and industrial coatings to protect metal surfaces from degradation caused by exposure to corrosive environments. It forms a protective film on metal surfaces, preventing the initiation and propagation of corrosion reactions.
- Surfactants: Dibenzylamine derivatives are utilized as surfactants and emulsifiers in personal care products, detergents, and industrial cleaners. They lower the surface tension between two immiscible phases, facilitating the formation of stable emulsions and enhancing the wetting, dispersing, and foaming properties of formulations.
- Polymer Additives: Dibenzylamine compounds are incorporated into polymer formulations as additives to modify the properties and performance of plastics, rubbers, and resins. They act as plasticizers, stabilizers, or crosslinking agents, improving the flexibility, durability, and thermal stability of polymer materials.
- Chemical Synthesis: Dibenzylamine is used as a catalyst or reagent in various chemical transformations, including hydrogenation, oxidation, and rearrangement reactions. It facilitates the conversion of starting materials into desired products with high efficiency and selectivity in organic synthesis.
- Pharmaceuticals: Dibenzylamine derivatives have pharmacological properties and find applications in the pharmaceutical industry as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or intermediates for the synthesis of therapeutic agents. They exhibit biological activities such as antimicrobial, antiviral, and antifungal properties.
- Gas Treatment: Dibenzylamine is utilized in gas treatment processes, such as gas sweetening and gas purification, to remove acidic impurities such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from natural gas streams. It reacts with acidic components to form non-corrosive and environmentally friendly salts.
- Flotation Agents: Dibenzylamine derivatives are employed as collectors or frothers in the flotation of minerals, ores, and metal concentrates in the mining industry. They selectively adsorb onto the surfaces of target minerals, facilitating their separation from gangue minerals in flotation cells.
- Electroplating: Dibenzylamine compounds are used in electroplating baths as additives to improve the efficiency and quality of metal deposition processes. They enhance the throwing power, leveling, and brightness of plated metal coatings on substrates in applications such as decorative and functional plating.
- Textile Auxiliaries: Dibenzylamine-based formulations are employed in the textile industry as dyeing assistants, leveling agents, and anti-creasing agents. They improve the dye uptake, color uniformity, and fabric softness in textile dyeing and finishing processes, enhancing the quality and appearance of dyed fabrics.