HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Pyridine

Product Description
Pyridine is a heterocyclic aromatic compound with various industrial applications.
Product:
Pyridine
CAS:
110-86-1
Synonym:
Azabenzene
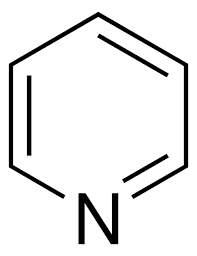
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless to yellow liquid
Boiling point
115 °C
Density
0.98 g/cm3
Flash Point
20 °C
Melting point
−42 °C
Molecular Weight
79.10
Odor
Nauseating fish-like odor
Purity
≥99.0%
Refractive index
1.509
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote



Pyridine used in many
industry applications
Pyridine is a heterocyclic aromatic compound with various industrial applications. Here are some of its industrial uses:
- Chemical Synthesis: Pyridine serves as a versatile building block and solvent in organic synthesis. It is used in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes, flavorings, and other fine chemicals.
- Pharmaceuticals: It is utilized in the pharmaceutical industry as a solvent, catalyst, and reagent in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Pyridine derivatives are found in many drugs and medications for various therapeutic applications.
- Agrochemicals: Pyridine is used in the production of herbicides, insecticides, fungicides, and other crop protection products. It serves as a precursor or intermediate in the synthesis of active ingredients for agricultural chemicals.
- Flavorings and Fragrances: Pyridine derivatives are used in the flavor and fragrance industry as synthetic intermediates and odorants. They may be employed in the synthesis of artificial flavors, fragrances, and aroma compounds for use in food, cosmetics, and perfumes.
- Solvents: Pyridine is used as a solvent for various chemical reactions and processes. It is particularly useful for dissolving polar and nonpolar compounds, making it suitable for use in organic synthesis, extraction, purification, and analysis.
- Rubber Industry: Pyridine is employed in the rubber industry as a vulcanization accelerator and antiozonant. It helps improve the curing and cross-linking of rubber compounds, enhancing the mechanical properties and durability of rubber products.
- Textile Industry: Pyridine derivatives may find applications in the textile industry for dyeing and finishing processes. They may serve as dye intermediates, leveling agents, or pH regulators to enhance the color uptake, uniformity, and fastness of textile dyes.
- Corrosion Inhibitors: Pyridine derivatives are used as corrosion inhibitors in metalworking fluids, lubricants, and coatings. They help protect metal surfaces from corrosion and degradation caused by exposure to corrosive environments such as moisture, acids, and salts.
- Analytical Chemistry: Pyridine is employed as a solvent and reagent in various analytical chemistry techniques such as chromatography and spectroscopy. It can be used for sample preparation, extraction, derivatization, and analysis of organic and inorganic compounds.
- Electronics: Pyridine-based compounds may find applications in the electronics industry for the production of electronic chemicals, solvents, and materials. They may be used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, printed circuit boards, and electronic components.