HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Heptanoic Acid

Product Description
Heptanoic acid, also known as enanthic acid, is a straight-chain fatty acid with various industrial applications.
Product:
Heptanoic Acid
CAS:
111-14-8
Synonym:
Enanthic acid; Oenanthic acid
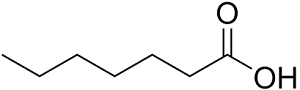
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Boiling point
223 °C
Density
0.918 g/cm3
Flash Point
110 °C
Melting point
-7.5 °C
Molecular Weight
130.18
Odor
Pungent odor
Purity
≥99%
Refractive index
1.423
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Heptanoic Acid
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Heptanoic Acid used in many
industry applications
Heptanoic acid, also known as enanthic acid, is a straight-chain fatty acid with various industrial applications. Here are some of its common uses:
- Fragrance and Flavoring Agent: Heptanoic acid is utilized in the fragrance and flavor industry as a component in perfumes, cosmetics, and food flavorings. It contributes to the aroma of certain fruits and has a fruity, slightly rancid odor.
- Chemical Intermediate: It serves as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, plasticizers, lubricants, and surfactants. Heptanoic acid can undergo esterification, oxidation, or halogenation reactions to produce derivatives with specific properties.
- Metalworking Fluids: Heptanoic acid is sometimes employed as a component in metalworking fluids, such as cutting oils and lubricants, due to its lubricating properties. It helps reduce friction and heat generation during metal cutting, milling, and grinding operations.
- Corrosion Inhibitor: In some industrial applications, heptanoic acid is used as a corrosion inhibitor for metals, particularly ferrous metals like steel and iron. It forms a protective film on the metal surface, preventing corrosion caused by exposure to moisture and aggressive chemicals.
- Adhesive Formulations: Heptanoic acid may be incorporated into adhesive formulations to improve adhesion to various substrates, such as metals, plastics, and ceramics. It enhances the wetting and spreading properties of adhesives, leading to stronger bonds and better performance.
- Surfactant: Some derivatives of heptanoic acid, such as heptanoate esters and sulfonates, can function as surfactants or emulsifiers in cleaning products, detergents, and personal care formulations. They help reduce surface tension and facilitate the dispersion of insoluble substances in aqueous solutions.
- Textile Industry: Heptanoic acid derivatives may find applications in the textile industry as softeners, lubricants, or antistatic agents for fibers, yarns, and fabrics. They impart desirable properties to textiles, such as smoothness, flexibility, and static control.
- Plasticizers: Certain esters of heptanoic acid can be used as plasticizers in polymer formulations to improve flexibility, elongation, and processability. They are commonly employed in the production of flexible PVC, synthetic rubbers, and other plastic materials.
- Animal Feed Additive: Heptanoic acid and its salts may be included in animal feed formulations as flavor enhancers or feed additives to improve palatability and digestion. They can stimulate appetite and promote the consumption of feed by livestock and poultry.