HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Diallyl Phthalate

Product Description
Diallyl Phthalate (DAP) is a chemical compound with several industrial applications.
Product:
Diallyl Phthalate
CAS:
131-17-9
Synonym:
Phthalic acid, diallyl ester; 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, di-2-propenyl ester
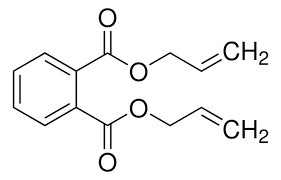
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Clear pale-yellow liquid
Boiling point
165-167 °C/5 mmHg
Density
1.121 g/cm3
Flash Point
166 °C
Melting point
-70 °C
Molecular Weight
246.26
Odor
Odorless
Purity
97%
Refractive index
1.519
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Diallyl Phthalate
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Diallyl Phthalate used in many
industry applications
Diallyl Phthalate (DAP) is a chemical compound with several industrial applications. Here are some of its primary uses:
- Thermosetting Plastics: DAP is commonly used as a crosslinking agent and monomer in the production of thermosetting plastics, such as epoxy resins. It reacts with other monomers or polymers under heat and pressure to form strong and durable plastic materials, suitable for various applications including coatings, laminates, and electrical insulators.
- Composite Materials: DAP is utilized as a crosslinking agent and reinforcement in the manufacturing of composite materials, particularly in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction. It enhances the mechanical properties, thermal stability, and chemical resistance of composite structures, making them lightweight yet strong and durable.
- Adhesives and Sealants: DAP serves as a crosslinking agent and modifier in the formulation of adhesives, sealants, and caulks. It improves the bonding strength, adhesion, and cohesive properties of adhesive formulations, ensuring reliable and long-lasting bonds between substrates in construction, automotive, and electronics applications.
- Molded Parts and Components: DAP is used in injection molding, compression molding, and casting processes to produce molded parts and components with high dimensional stability, heat resistance, and chemical inertness. It is employed in the manufacturing of automotive parts, electrical enclosures, and industrial equipment.
- Electrical Insulation: DAP-based materials are utilized in electrical and electronic applications as insulating materials for cables, wires, and electronic components. They provide excellent electrical insulation properties, thermal conductivity, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, ensuring safe and reliable operation of electrical systems.
- Coatings and Finishes: DAP is incorporated into coatings, paints, and surface finishes to improve their adhesion, durability, and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and weathering. It is used in architectural coatings, industrial coatings, and marine coatings to protect and enhance the appearance of surfaces exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
- Rubber Vulcanization: DAP is employed as a crosslinking agent in the vulcanization process of rubber compounds to improve their mechanical properties, aging resistance, and dimensional stability. It enhances the strength, elasticity, and durability of rubber products such as tires, conveyor belts, and gaskets.
- Textile Treatment: DAP-based formulations are used in textile finishing processes to impart crease resistance, wrinkle resistance, and dimensional stability to fabrics. They are applied to textiles through padding, spraying, or coating methods to enhance their performance and appearance in apparel, home furnishings, and industrial textiles.
- Oil and Gas Industry: DAP-based materials are employed in oilfield applications as sealing compounds, gasket materials, and downhole components. They provide reliable sealing and corrosion resistance in drilling, completion, and production operations, ensuring the integrity and safety of oil and gas equipment and infrastructure.