HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Zinc Dibutyldithiocarbamate

Product Description
Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate is a chemical compound with various industrial applications.
Product:
Zinc Dibutyldithiocarbamate
CAS:
136-23-2
Synonym:
Zinc(II) dibutyldithiocarbamate; Carbamodithioic acid, dibutyl-, zinc complex; Dibutyldithiocarbamic acid, zinc salt
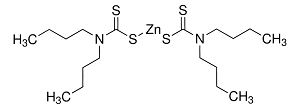
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White powder
Boiling point
296 °C (decomposes)
Density
1.24 g/cm3
Melting point
104-108 °C
Molecular Weight
474.14
Odor
Pleasant odor
Purity
99%
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Zinc Dibutyldithiocarbamate
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Zinc Dibutyldithiocarbamate used in many
industry applications
Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate is a chemical compound with various industrial applications. Here are some of its main uses:
- Rubber Vulcanization Accelerator: Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate is commonly used as a rubber vulcanization accelerator in the production of tires, conveyor belts, seals, and other rubber products. It accelerates the crosslinking reaction between rubber polymer chains and sulfur, leading to the formation of a network structure that improves the strength, elasticity, and durability of rubber compounds. Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate is particularly effective in promoting rapid vulcanization at low temperatures, reducing processing times and energy consumption in rubber manufacturing.
- Antioxidant: This compound exhibits antioxidant properties and is employed in the stabilization of rubber and polymer materials against oxidative degradation. It can scavenge free radicals and inhibit chain reactions associated with oxidation processes, thereby extending the service life and performance of rubber products exposed to environmental factors such as heat, oxygen, and UV radiation. Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate-based formulations help prevent premature aging, cracking, and degradation in rubber components used in automotive, construction, and industrial applications.
- Antiozonant: Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate serves as an antiozonant or ozone cracking inhibitor in rubber formulations exposed to ozone-rich environments. Ozone can react with unsaturated bonds in rubber polymers, leading to the formation of cracks and surface degradation known as ozone cracking. Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate compounds form a protective barrier on the rubber surface, absorbing and neutralizing ozone molecules to prevent the onset of cracking and maintain the integrity of rubber products used in outdoor and automotive applications.
- Fungicide and Bactericide: Due to its biocidal properties, zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate is utilized as a fungicide and bactericide in various industrial and agricultural applications. It can inhibit the growth of fungi, bacteria, and algae on surfaces and in aqueous systems, providing protection against microbial contamination and deterioration. Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate-based formulations are used in wood preservatives, metalworking fluids, paints, coatings, and agricultural chemicals to prevent mold growth, rot, and corrosion, thereby extending the service life and performance of treated materials.
- Plastic Additive: Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate may be used as an additive in plastic and polymer formulations to enhance processing and performance properties. It can improve the flow characteristics, thermal stability, and UV resistance of plastics during processing and end-use applications. Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate-based additives help optimize the rheological properties, surface finish, and dimensional stability of plastic products, making them suitable for a wide range of applications in automotive, construction, packaging, and consumer goods industries.
- Adhesive Formulation: This compound is employed in the formulation of adhesives and sealants as a curing agent or crosslinking agent. It promotes the crosslinking of polymer chains in adhesive formulations, leading to the formation of strong and durable bonds between substrates. Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate-based adhesives exhibit excellent adhesion, cohesion, and chemical resistance properties, making them suitable for bonding rubber, metal, plastic, and composite materials in automotive, construction, and industrial assembly applications.
- Textile Chemicals: Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate is used in the textile industry as an antimicrobial agent and preservative in textile processing chemicals. It helps prevent microbial growth and contamination in textile fibers, yarns, and fabrics during manufacturing, storage, and transportation. Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate-based formulations contribute to the preservation of textile products and ensure compliance with quality and safety standards in textile manufacturing and finishing processes.
- Paints and Coatings: Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate is employed as a drier or catalyst in the formulation of paints, coatings, and inks. It accelerates the drying and curing of solvent-based and water-based coatings by promoting the oxidative crosslinking of binder polymers. Zinc dibutyldithiocarbamate-based driers enhance the film formation, hardness, and adhesion properties of coatings, leading to improved durability, weatherability, and corrosion resistance in architectural, automotive, marine, and industrial coatings applications.