Pharmaceutical & Fine Chemicals
Thiourea Dioxide

Product Description
Thiourea dioxide, also known as formamidine sulfinic acid, is a versatile compound with various industrial applications due to its unique properties.
Product:
Thiourea Dioxide
CAS:
1758-73-2
Synonym:
Formamidine sulfinic acid; Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid
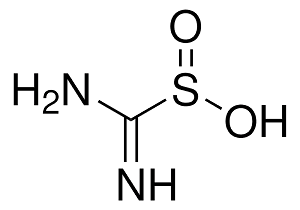
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White or light-yellow crystalline powder
Density
1.68 g/cm3
Melting point
124-127 °C (dec.)
Molecular Weight
108.12
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥98%
Refractive index
1.6550
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote
We Offer Thiourea Dioxide
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Thiourea Dioxide used in many
industry applications
Thiourea dioxide, also known as formamidine sulfinic acid, is a versatile compound with various industrial applications due to its unique properties. Here are some of its notable industrial uses:
- Textile Industry: Thiourea dioxide is widely used as a reducing agent in textile processing, particularly in the bleaching and dyeing of fibers such as cotton, wool, and silk. It effectively removes color impurities and improves the brightness and fastness of dyed fabrics, enhancing their aesthetic appeal and marketability.
- Paper Pulp Bleaching: In the paper and pulp industry, thiourea dioxide serves as a bleaching agent for wood pulp and recycled paper materials. It efficiently decolorizes lignin and other chromophores present in pulp fibers, resulting in the production of high-quality, bright white paper products with superior printability and readability.
- Photography: Thiourea dioxide is used in photographic developing solutions as a fixing agent for black and white photographic prints. It assists in the removal of unexposed silver halide crystals from photographic emulsions, stabilizing the image and preventing undesired discoloration or fading during processing and storage.
- Chemical Synthesis: Thiourea dioxide serves as a versatile intermediate and reducing agent in organic synthesis reactions, including the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals. It participates in various transformations such as reductive amination, thioamination, and sulfur dioxide fixation, enabling the efficient synthesis of complex molecules and functional materials.
- Electroplating: In electroplating processes, thiourea dioxide is utilized as a selective reducing agent for metal ion deposition onto conductive substrates. It enables the electrodeposition of metals such as copper, nickel, and silver with high purity and uniformity, contributing to the fabrication of corrosion-resistant coatings, decorative finishes, and electronic components.
- Water Treatment: Thiourea dioxide is employed in water treatment applications as a dechlorination agent for removing residual chlorine and chloramines from drinking water, wastewater, and swimming pools. It effectively neutralizes chlorine-based disinfectants without generating harmful byproducts, ensuring the safety and quality of treated water for human consumption and recreational use.
- Chemical Analysis: Thiourea dioxide is utilized in analytical chemistry as a reducing agent and spectrophotometric reagent for the determination of various metal ions and organic compounds. It reacts selectively with specific analytes to form colorimetric complexes or precipitates, enabling their quantitative analysis and detection in complex matrices.