HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Sodium Thiocyanate

Product Description
Sodium thiocyanate is an organic sodium salt which is the monosodium salt of thiocyanic acid. It is one of the main sources of the thiocyanate ion.
Product:
Sodium Thiocyanate
CAS:
540-72-7
Synonym:
Sodium isothiocyanate; Sodium rhodanate; Sodium rhodanide; Sodium sulfocyanate
Structure:
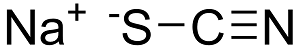
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystalline powder
Density
1.735 g/cm3
Melting point
287 °C
Molecular Weight
81.07
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥98%
Refractive index
1.545
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote
We Offer Sodium Thiocyanate
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Sodium Thiocyanate used in many
industry applications
Sodium thiocyanate, a white crystalline solid, finds various industrial applications owing to its unique properties. Here's a list of some of its industrial uses:
- Photography: Sodium thiocyanate is used in photography as a fixing agent for developing photographic films and prints, where it helps dissolve and remove unexposed silver halide crystals from the emulsion, stabilizing the final image.
- Textile Industry: It is employed in the textile industry for dyeing and printing applications, where it acts as a leveling agent and mordant to improve color fastness and dye penetration on fabrics and fibers.
- Chemical Synthesis: Sodium thiocyanate serves as a precursor in various chemical synthesis reactions, including the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals, where it provides a source of thiocyanate ions.
- Metal Plating: It is used in electroplating baths as a complexing agent for metal ions, such as silver, copper, and zinc, to improve the uniformity and adhesion of metal coatings on substrates in metal finishing and surface treatment processes.
- Deicing Agent: Sodium thiocyanate is utilized as a deicing agent for airport runways, roads, and sidewalks in cold climates, where it lowers the freezing point of water and melts ice and snow effectively.
- Chemical Analysis: It is used in chemical analysis techniques, such as titration and spectrophotometry, for the determination of various analytes, including iron, copper, and silver ions, in aqueous solutions.