Pharmaceutical & Fine Chemicals
HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Thiourea

Product Description
Thiourea is an organosulfur compound.
Product:
Thiourea
CAS:
62-56-6
Synonym:
Sulfourea; Thiocarbamide
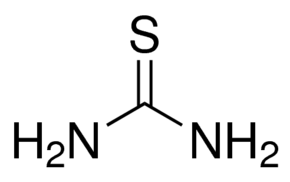
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystals
Boiling point
263.89°C
Density
1.405 g/cm3
Melting point
170 - 176 °C
Molecular Weight
76.12
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥ 99.0 %
Refractive index
1.5300
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote



Thiourea used in many
industry applications
Thiourea, a white crystalline compound, finds various industrial applications owing to its unique properties. Here's a list of some of its industrial uses:
- Chemical Synthesis: Thiourea is widely used as a raw material and intermediate in organic synthesis reactions, including the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes, and rubber chemicals.
- Metal Processing: It serves as a complexing agent and leaching agent in metal processing and mining operations, where it facilitates the extraction and purification of metals, such as gold, silver, and copper, from ores and concentrates.
- Textile Industry: Thiourea is employed in the textile industry for textile dyeing and printing applications, where it acts as a reducing agent, mordant, and fixing agent for reactive dyes and sulfur dyes on natural and synthetic fibers.
- Photography: It is used in photography as a fixing agent and toner in photographic development processes, where it helps dissolve and remove unexposed silver halide crystals from the emulsion and produces stable image tones.
- Electroplating: Thiourea is utilized as a complexing agent and brightener in electroplating baths for the deposition of metal coatings, such as silver, gold, and nickel, on metal substrates, where it improves adhesion, brightness, and distribution of the plated layer.
- Adhesives and Sealants: It is used as a catalyst and curing agent in the production of adhesives, sealants, and rubber compounds, where it promotes cross-linking and polymerization reactions to improve adhesive strength, durability, and chemical resistance.
- Medicine: Thiourea has pharmaceutical applications, particularly in the treatment of hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer, where it acts as a thyroid inhibitor by interfering with the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
- Chemical Analysis: It is employed in chemical analysis techniques, such as spectrophotometry and chromatography, for the determination of various analytes, including metal ions, amino acids, and proteins, in biological and environmental samples.
- Waste Water Treatment: Thiourea is used in wastewater treatment processes for the removal of heavy metals and cyanides, where it forms stable complexes with metal ions and facilitates their precipitation or adsorption onto solid substrates.
- Fire Retardants: It serves as a flame retardant and smoke suppressant in plastics, textiles, and coatings, where it reduces flammability and smoke generation by releasing nitrogen-containing gases and forming charred protective layers.