HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Dibenzylhydroxylamine

Product Description
Dibenzylhydroxylamine is a chemical compound that finds applications in various industrial processes.
Product:
Dibenzylhydroxylamine
CAS:
621-07-8
Synonym:
Benzyl Hydroxylamine; N,N-Dibenzylhydroxylamine
Structure:
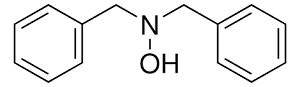
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystals
Density
1.0439 g/cm3
Melting point
125-128 °C
Molecular Weight
213.28
Purity
98%
Refractive index
1.5300
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote
We Offer Dibenzylhydroxylamine
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Dibenzylhydroxylamine used in many
industry applications
Dibenzylhydroxylamine is a chemical compound that finds applications in various industrial processes. Here are some of its primary uses:
- Antioxidant: Dibenzylhydroxylamine is utilized as an antioxidant additive in lubricants, polymers, and rubber compounds to prevent or retard oxidative degradation. It scavenges free radicals and reactive oxygen species, thereby extending the service life and improving the performance of materials exposed to oxidative environments.
- Corrosion Inhibitor: Dibenzylhydroxylamine is employed as a corrosion inhibitor in metalworking fluids, industrial coatings, and aqueous solutions to protect metal surfaces from corrosion caused by exposure to aggressive environments. It forms a protective film on metal surfaces, preventing the initiation and propagation of corrosion reactions.
- Polymer Stabilizer: Dibenzylhydroxylamine acts as a stabilizer or inhibitor in polymer formulations to prevent degradation reactions induced by heat, light, or oxidative conditions. It inhibits chain scission, crosslinking, and discoloration reactions, thereby maintaining the integrity and appearance of polymer materials during processing and use.
- Rubber Antidegradant: Dibenzylhydroxylamine serves as an antidegradant additive in rubber compounds, particularly in tires, conveyor belts, and automotive parts, to enhance their resistance to aging, cracking, and deterioration. It inhibits the degradation of rubber polymers caused by heat, oxygen, ozone, and flexural fatigue.
- Fuel Additive: Dibenzylhydroxylamine is used as a fuel additive in gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuels to improve their stability, cleanliness, and combustion efficiency. It inhibits the formation of gum, varnish, and deposits in fuel systems and combustion chambers, reducing engine fouling and maintenance costs.
- Emulsion Polymerization: Dibenzylhydroxylamine is employed as a polymerization inhibitor or chain transfer agent in emulsion polymerization processes to control the molecular weight, polymer morphology, and particle size of latex particles. It regulates the polymerization kinetics and suppresses the formation of oversized particles or gel-like structures.
- Photographic Chemical: Dibenzylhydroxylamine is used as a photographic developer or fixing agent in black-and-white photography processes to reduce or eliminate residual silver halide from photographic prints or films. It accelerates the development of latent image grains and facilitates the removal of unexposed silver halide crystals.
- Water Treatment: Dibenzylhydroxylamine is employed in water treatment applications as an oxygen scavenger or corrosion inhibitor in boiler feedwater, cooling water, and industrial process water systems. It reacts with dissolved oxygen or metal ions to inhibit corrosion and scale formation on metal surfaces, prolonging equipment life.
- Textile Auxiliaries: Dibenzylhydroxylamine-based formulations are used in the textile industry as dyeing assistants, leveling agents, and anti-creasing agents. They improve the dye uptake, color uniformity, and fabric softness in textile dyeing and finishing processes, enhancing the quality and appearance of dyed fabrics.