Potassium Iodide

Product Description
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound with various industrial applications.
Product:
Potassium Iodide
CAS:
7681-11-0
Synonym:
Potassium salt of hydriodic acid; Iodic acid potassium salt; Potassium monoiodide; Knollide
Structure:
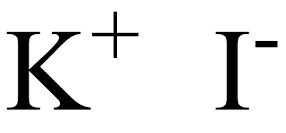
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless or white crystals
Boiling point
1323 °C
Density
3.13 g/cm3
Melting point
681 °C
Molecular Weight
166.00
Odor
Odorless
Purity
≥99%
Refractive index
1.677
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote
We Offer Potassium Iodide
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Potassium Iodide used in many
industry applications
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound with various industrial applications. Here are some of its main uses:
- Pharmaceuticals: Potassium iodide is commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry as a source of iodine for the production of medications. It is employed in the formulation of oral solutions, tablets, and topical preparations for the treatment of thyroid disorders, including hyperthyroidism, thyroid storm, and iodine deficiency. Potassium iodide helps to regulate thyroid function and prevent the development of goiter by providing the essential nutrient iodine.
- Photography: It serves as a key ingredient in photographic chemicals and developers for black-and-white film and paper processing. Potassium iodide is utilized to promote the formation of silver iodide, a light-sensitive compound, during the sensitization and development stages of photographic printing. It enhances the sensitivity and contrast of photographic emulsions, allowing for the production of high-quality images with fine detail and tonal range.
- Food Additive: Potassium iodide is approved for use as a food additive and dietary supplement in certain jurisdictions. It may be added to table salt, processed foods, and nutritional supplements to fortify them with iodine, an essential micronutrient required for thyroid hormone synthesis and metabolism. Potassium iodide helps to prevent iodine deficiency disorders, such as hypothyroidism, mental retardation, and goiter, by ensuring adequate iodine intake through the diet.
- Chemical Synthesis: It serves as a versatile reagent and precursor in organic synthesis reactions for the preparation of various organic and inorganic compounds. Potassium iodide is utilized as a source of iodine atoms in substitution, addition, and oxidation reactions, facilitating the introduction of iodine-containing functional groups into organic molecules. It is employed in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates, fine chemicals, agrochemicals, and specialty materials.
- Laboratory Reagent: Potassium iodide is widely used as a laboratory reagent and analytical standard in chemical research, education, and analysis. It is employed in qualitative and quantitative tests for the detection, identification, and quantification of substances in chemical, biological, and environmental samples. Potassium iodide reacts with various analytes to form colored complexes, precipitates, or oxidation products, which can be measured or visually observed for analytical purposes.
- Medical Radioprotection: Potassium iodide is utilized in emergency preparedness and radiological protection measures to prevent or reduce the risk of radiation-induced thyroid cancer following exposure to radioactive iodine isotopes, such as iodine-131. It can be administered orally as a thyroid-blocking agent before or shortly after radiation exposure to saturate the thyroid gland with stable iodine, thereby inhibiting the uptake and retention of radioactive iodine and minimizing the potential for thyroid damage.
- Chemical Etching: It is employed in metalworking and semiconductor industries as an etchant or etching solution for the selective removal of metal oxides, oxides, and films from metal surfaces, electronic components, and optical substrates. Potassium iodide solutions are used in chemical etching processes to clean, polish, and pattern metal surfaces, remove surface contaminants, and create microstructures or surface textures with high precision and reproducibility.
- Textile Dyeing and Printing: Potassium iodide finds applications in the textile industry as a mordant or dyeing auxiliary for natural and synthetic fibers. It is utilized to enhance the color fastness, brightness, and uniformity of textile dyes by promoting their adsorption and fixation onto fabric surfaces. Potassium iodide can facilitate the dyeing and printing of cotton, wool, silk, polyester, and other fibers with acid, direct, and reactive dyes in various shades and patterns.