Lithium Battery & Electrolyte Chemicals
Tetramethylguanidine

Product Description
Tetramethylguanidine is a chemical compound with various industrial applications.
Product:
Tetramethylguanidine
CAS:
80-70-6
Synonym:
1,1,3,3-Tetramethylguanidine; N,N,N',N'-Tetramethylguanidine
Structure:
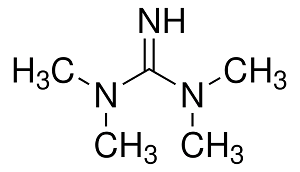
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Boiling point
162-163 °C
Density
0.918 g/cm3
Flash Point
60 °C
Melting point
−30 °C
Molecular Weight
115.18
Odor
Mild Ammoniacal odor
Purity
99%
Refractive index
1.469
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote
We Offer Tetramethylguanidine
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Tetramethylguanidine used in many
industry applications
Tetramethylguanidine is a chemical compound with various industrial applications. Here are some of its main uses:
- Catalyst in Organic Synthesis: Tetramethylguanidine serves as a powerful organic base and catalyst in various synthetic transformations. It is commonly employed in reactions such as esterifications, aldol condensations, and Michael additions. Due to its high basicity and nucleophilicity, it facilitates the formation of new bonds and the synthesis of complex molecules in organic chemistry.
- Blowing Agent in Polyurethane Foam Production: It is utilized as a blowing agent in the production of polyurethane foams. When added to polyol formulations along with isocyanates, tetramethylguanidine reacts with the isocyanate groups to release carbon dioxide gas, leading to the expansion and formation of foam structures. Polyurethane foams produced using tetramethylguanidine as a blowing agent find applications in insulation, cushioning, and packaging materials.
- Stabilizer in Polymerization Reactions: Tetramethylguanidine is employed as a stabilizer or inhibitor in polymerization reactions, particularly in the production of acrylic and methacrylic polymers. It helps control the polymerization process by scavenging trace impurities, such as acids and moisture, which can act as initiators or inhibitors of polymerization. This ensures the formation of high-quality polymers with desired molecular weights and properties.
- Intermediate in Pharmaceutical Synthesis: It serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds and active ingredients. Tetramethylguanidine-containing derivatives are used in the preparation of various drugs, including antiviral agents, antimalarial drugs, and anticancer medications. Its role as a building block in organic synthesis enables the efficient production of diverse pharmaceutical products.
- Textile Auxiliary: Tetramethylguanidine finds applications in the textile industry as a dye auxiliary agent and pH regulator. It is used to adjust the pH of dye baths and textile finishing processes, ensuring optimal conditions for dye uptake, color development, and fiber treatment. Additionally, tetramethylguanidine may serve as a catalyst or modifier in certain textile chemical processes.
- Antioxidant Additive: It is sometimes employed as an antioxidant additive in industrial fluids and lubricants to inhibit the oxidation of organic compounds and prevent the formation of harmful degradation products. Tetramethylguanidine can scavenge free radicals and reactive oxygen species, thereby extending the shelf life and stability of lubricating oils, hydraulic fluids, and other industrial products.
- Electrolyte Additive in Lithium-Ion Batteries: In lithium-ion battery electrolytes, tetramethylguanidine can be used as an additive to improve battery performance and stability. It helps enhance the conductivity and cycling stability of lithium-ion batteries by optimizing the electrolyte composition and mitigating undesirable side reactions at the electrode-electrolyte interface.
- Reagent in Organic Synthesis Laboratories: Tetramethylguanidine is widely utilized as a reagent and reactivity modifier in organic synthesis laboratories. Its versatility and effectiveness in various chemical transformations make it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners working on the development of new synthetic methodologies and the synthesis of complex molecules.
- Chemical Intermediate: It serves as a versatile chemical intermediate for the synthesis of specialty chemicals, surfactants, and functional materials. Tetramethylguanidine-containing compounds find applications in diverse industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, coatings, and personal care products, where they impart desired properties and functionalities to end products.