HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate

Product Description
2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate is an acrylic monomer building block used as a feedstock chemical for synthesis and polymer manufacturing.
Product:
2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate
CAS:
868-77-9
Synonym:
HEMA; Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate; 2-Propenoic acid 2-methyl- 2-hydroxyethyl ester
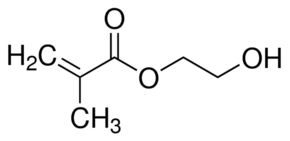
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless Liquid
Boiling point
205 - 208 °C
Density
1.073 g/cm3
Flash Point
97°C
Melting point
-12 °C
Molecular Weight
130.14
Odor
Sweet, fruity, or honey-like odor
Refractive index
1.453
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate used in many
industry applications
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) is a chemical compound with various industrial applications. Here's a list of some of its uses:
- Dental Materials: HEMA is commonly used in the production of dental materials, such as dental adhesives, sealants, and composite resins. It improves adhesion to tooth structure and provides flexibility and durability to dental restorations.
- Medical Devices: It is utilized in the manufacture of medical devices, such as contact lenses, intraocular lenses, and wound dressings. HEMA-based materials offer biocompatibility, water absorption properties, and optical clarity in medical applications.
- Hydrogels: HEMA is used in the production of hydrogels for various biomedical and pharmaceutical applications, including drug delivery systems, wound healing, and tissue engineering scaffolds. Hydrogels based on HEMA exhibit high water absorption and biocompatibility.
- Coatings and Adhesives: It serves as a monomer in the formulation of coatings, adhesives, and sealants for various applications, including construction, automotive, and electronics. HEMA-based coatings offer flexibility, adhesion, and weather resistance.
- Personal Care Products: HEMA is used in the production of personal care products, such as hair styling gels, nail polishes, and skin creams. It provides film-forming properties, adhesion, and water resistance in cosmetic formulations.
- Textile Treatment: It is employed in textile treatment formulations as a crosslinking agent and modifier to impart wrinkle resistance, crease recovery, and colorfastness to fabrics. HEMA-based finishes enhance the performance and appearance of textiles.
- Optical Materials: HEMA is used in the production of optical materials, such as ophthalmic lenses and contact lens coatings. It offers optical clarity, UV resistance, and compatibility with other monomers in optical formulations.
- Hygiene Products: It is used in the manufacture of hygiene products, such as absorbent pads, wound dressings, and diapers. HEMA-based materials provide moisture absorption properties and comfort in hygiene applications.
- Photopolymer Resins: HEMA is employed as a monomer in photopolymer resins for stereolithography (SLA) and digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing. It enables rapid polymerization and high-resolution printing of 3D objects.
- Industrial Coatings: HEMA is used in the formulation of industrial coatings for metal, wood, and plastic substrates. It provides adhesion, flexibility, and chemical resistance in coatings for corrosion protection and decorative purposes.