HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Dimethyl Phosphite

Product Description
Dimethyl phosphite is a chemical compound with various industrial and commercial applications.
Product:
Dimethyl Phosphite
CAS:
868-85-9
Synonym:
Phosphonic acid, dimethyl ester; Dimethyl phosphonate
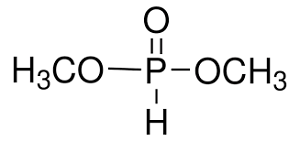
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Boiling point
170-171 °C
Density
1.200 g/cm3
Flash Point
70 °C
Melting point
29 °C
Molecular Weight
110.05
Odor
Mild odor
Purity
98%
Refractive index
1.402
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Dimethyl Phosphite
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Dimethyl Phosphite used in many
industry applications
Dimethyl phosphite is a chemical compound with various industrial and commercial applications. Here are some of its uses:
- Agrochemicals: Dimethyl phosphite is used in the production of agrochemicals such as herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides. It serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of phosphonate-based active ingredients that help control pests and diseases in crops.
- Flame Retardants: Dimethyl phosphite is used as a flame retardant additive in plastics, polymers, and coatings. It can improve the fire resistance and self-extinguishing properties of materials by releasing phosphorus-containing compounds that act as char formers and suppressants of combustion.
- Chemical Synthesis: Dimethyl phosphite is used as a reagent or building block in various organic synthesis reactions. It can be employed in the production of pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and specialty compounds through processes such as esterification, phosphorylation, and hydrophosphonylation.
- Polymerization: Dimethyl phosphite is used as a monomer or comonomer in the polymerization of certain plastics and resins. It can contribute to the formation of phosphorus-containing polymers with enhanced thermal stability, flame retardancy, and mechanical properties.
- Catalysis: Dimethyl phosphite can serve as a ligand or catalyst precursor in organometallic catalysis and coordination chemistry. It may facilitate various chemical transformations such as hydrogenation, hydroformylation, and cross-coupling reactions through coordination with transition metal complexes.
- Pharmaceutical Intermediates: Dimethyl phosphite is used in the pharmaceutical industry as an intermediate in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and drug intermediates. It may be incorporated into drug molecules to introduce phosphorus-containing functional groups or to modify their pharmacokinetic properties.
- Electroplating: Dimethyl phosphite is used in electroplating baths as a source of phosphorus for the deposition of metal coatings. It can help improve the adhesion, corrosion resistance, and solderability of plated layers on metal substrates.
- Textile Auxiliaries: Dimethyl phosphite may be used in the textile industry as a flame retardant or finishing agent for fabrics and textiles. It can impart flame resistance to textiles without adversely affecting their physical or aesthetic properties.
- Oilfield Chemicals: Dimethyl phosphite is used in the oil and gas industry as a corrosion inhibitor and scale inhibitor in drilling fluids and production fluids. It helps protect metal equipment and pipelines from corrosion and scale deposition in harsh downhole environments.
- Adhesives and Sealants: Dimethyl phosphite may be used as a cross-linking agent or modifier in the formulation of adhesives, sealants, and coatings. It can improve the adhesion, flexibility, and chemical resistance of these products.