Polyetheramine

Product Description
Polyetheramine is a versatile compound with a wide range of industrial applications, owing to its unique properties and chemical structure.
Product:
Polyetheramine
CAS:
9046-10-0
Synonym:
Polypropylene glycol diamine; Diaminopolypropylene glycol; Pyrrolidine-3,4-diol
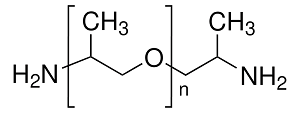
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Light yellow liquid
Boiling point
250 °C
Density
0.9978 g/cm3
Flash Point
234 °C
Melting point
-29 °C
Molecular Weight
~2000
Odor
Amine-like odor
Purity
97%
Refractive index
1.452
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Polyetheramine
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Polyetheramine used in many
industry applications
Polyetheramine is a versatile compound with a wide range of industrial applications, owing to its unique properties and chemical structure. Here are some of its industrial uses:
- Epoxy Resins: Polyetheramine serves as a curing agent or hardener for epoxy resins in various applications, including coatings, adhesives, and composites. It reacts with epoxy groups to form crosslinked networks, enhancing the mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability of the cured materials.
- Adhesives: Polyetheramine is utilized in the formulation of structural adhesives and sealants for bonding substrates in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. It provides excellent adhesion to a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, resulting in durable and high-performance adhesive joints.
- Coatings: Polyetheramine is incorporated into coatings formulations as a curing agent or crosslinker for various substrates, including metals, concrete, and wood. It promotes rapid curing and film formation, resulting in coatings with enhanced durability, weather resistance, and chemical protection.
- Fuel Additives: Polyetheramine is used as a fuel additive to improve the performance and efficiency of gasoline and diesel engines. It acts as a detergent and dispersant, preventing the formation of deposits and reducing engine fouling, leading to cleaner combustion and reduced emissions.
- Polyurethane Foams: Polyetheramine serves as a chain extender or crosslinker in the production of polyurethane foams for insulation, cushioning, and packaging applications. It reacts with isocyanate groups to form urea linkages, contributing to the cellular structure and mechanical properties of the foam.
- Textile Chemicals: Polyetheramine is employed in the textile industry as a softening agent or antistatic agent for fabrics and fibers. It imparts a soft and smooth feel to textiles, reduces static electricity buildup, and enhances the dyeing and finishing processes.
- Water Treatment: Polyetheramine is used in water treatment formulations as a dispersant, scale inhibitor, or corrosion inhibitor. It helps prevent the formation of scale deposits, disperses suspended solids, and protects metal surfaces from corrosion in cooling water systems, boilers, and reverse osmosis membranes.
- Personal Care Products: Polyetheramine is incorporated into personal care products, such as shampoos, conditioners, and skincare formulations, as a conditioning agent or emulsifier. It improves the texture, spreadability, and conditioning properties of cosmetic products, enhancing their performance and consumer appeal.
- Oilfield Chemicals: Polyetheramine is used in the oil and gas industry as a demulsifier, corrosion inhibitor, or friction reducer in drilling fluids and production chemicals. It helps improve the efficiency of drilling operations, prevents equipment corrosion, and reduces friction during oil and gas extraction processes.