Phenothiazine

Product Description
Phenothiazine is a heterocyclic compound with various industrial applications due to its unique properties.
Product:
Phenothiazine
CAS:
92-84-2
Synonym:
10H-Phenothiazine; Dibenzothiazine; Thiodiphenylamine
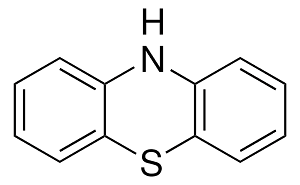
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Grayish-green to greenish-yellow solid
Boiling point
371 °C
Density
1.34 g/cm3
Flash Point
202 °C
Melting point
182-187 °C
Molecular Weight
199.27
Odor
Slight odor
Purity
≥98%
Refractive index
1.6353
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
Markets
get a quote
We Offer Phenothiazine
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Phenothiazine used in many
industry applications
Phenothiazine is a heterocyclic compound with various industrial applications due to its unique properties. Here are some of its main uses:
- Pharmaceuticals: Phenothiazine and its derivatives have long been utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for their diverse pharmacological properties. They are employed as antipsychotic agents in the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Additionally, phenothiazine derivatives have demonstrated antimicrobial, antihistaminic, and antiemetic activities, making them valuable components in the formulation of medications for infectious diseases, allergies, and nausea.
- Veterinary Medicine: Phenothiazine-based compounds are commonly used in veterinary medicine for their anthelmintic (anti-parasitic) properties. They are administered to livestock and companion animals to prevent and treat parasitic infections caused by nematodes and other gastrointestinal parasites. Phenothiazine derivatives exert their anthelmintic effects by disrupting the neuromuscular function of parasites, leading to paralysis and expulsion from the host's digestive tract.
- Chemical Synthesis: Phenothiazine serves as a versatile building block in organic synthesis, enabling the preparation of various functionalized derivatives with diverse chemical properties. It undergoes numerous chemical transformations, including oxidation, reduction, alkylation, and halogenation, to produce intermediates and final products used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes, and specialty chemicals.
- Antioxidants: Phenothiazine derivatives exhibit antioxidant properties and are employed as additives in rubber and polymer formulations to prevent degradation caused by exposure to oxygen, light, and heat. They act as free radical scavengers, inhibiting oxidative processes that lead to polymer chain scission, cross-linking, and loss of mechanical properties. Phenothiazine-based antioxidants are particularly useful in applications where stability and durability are critical, such as in the production of tires, cables, and plastics.
- Photographic Chemicals: Phenothiazine has been used historically in the photographic industry as a sensitizer and stabilizer in black-and-white photographic emulsions. It enhances the sensitivity of photographic films and papers to light, allowing for the production of high-quality images with improved contrast and tonal range. Phenothiazine derivatives are also employed as dye-forming couplers and developers in color photography processes.
- Electrochemical Devices: Phenothiazine-based compounds are utilized in electrochemical devices and energy storage systems due to their redox activity and electrochemical stability. They serve as mediators and redox shuttles in rechargeable batteries, fuel cells, and electrochemical sensors, facilitating electron transfer reactions and improving device performance and cycle life.
- Textile Industry: Phenothiazine derivatives find applications in the textile industry as colorants and dye intermediates. They are used to impart various shades of blue, green, and violet to textile fibers, yarns, and fabrics through dyeing and printing processes. Phenothiazine-based dyes exhibit good lightfastness, washfastness, and color retention properties, making them suitable for use in a wide range of textile applications, including apparel, home furnishings, and industrial textiles.
- Biological Research: Phenothiazine compounds are valuable tools in biological research and biochemistry studies due to their interactions with biological molecules and cellular processes. They are utilized as fluorescent probes, enzyme inhibitors, and modulators of ion channels and neurotransmitter receptors in experimental systems. Phenothiazine derivatives have also been investigated for their potential therapeutic applications in cancer therapy, neurodegenerative diseases, and infectious diseases.
- Agrochemicals: Phenothiazine-based compounds have pesticidal properties and are used in the formulation of insecticides, fungicides, and herbicides for agricultural applications. They act as broad-spectrum pesticides, targeting various pests, pathogens, and weeds that threaten crop yields and plant health. Phenothiazine derivatives may be applied as foliar sprays, soil treatments, or seed treatments to protect crops from pests and diseases and enhance agricultural productivity.
- Plasticizers: Phenothiazine derivatives have plasticizing properties and are utilized as additives in polymer formulations to improve flexibility, durability, and processability. They act as internal lubricants and softeners, reducing the glass transition temperature and enhancing the melt flow of thermoplastics and elastomers. Phenothiazine-based plasticizers are commonly used in the production of PVC compounds, rubber products, adhesives, and sealants.