HI! I’M ELEMENT AI.
Methyl Acrylate

Product Description
Methyl acrylate is an organic compound, more accurately the methyl ester of acrylic acid.
Product:
Methyl Acrylate
CAS:
96-33-3
Synonym:
Acrylic acid methyl ester; Methyl propenoate; 2-Propenoic acid, methyl ester
Structure:
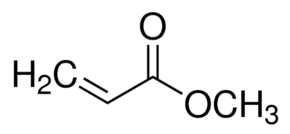
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless volatile liquid
Boiling point
79 - 80 °C
Density
0.96 g/cm3
Melting point
- 76.5 °C
Molecular Weight
86.1
Odor
Acrid odor
Purity
99.5 % Min
Refractive index
1.4003
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Methyl Acrylate
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Methyl Acrylate used in many
industry applications
Methyl acrylate, a colorless liquid with a sharp odor, finds various industrial applications owing to its unique properties. Here's a list of some of its industrial uses:
- Monomer: Methyl acrylate is primarily used as a monomer in the production of various polymers and copolymers, including acrylic resins, emulsions, and elastomers, through processes such as solution polymerization, emulsion polymerization, and bulk polymerization.
- Adhesives and Sealants: It serves as a raw material in the formulation of adhesives, sealants, and caulks, where it provides adhesion, flexibility, and weather resistance to the final products.
- Paints and Coatings: Methyl acrylate is employed as a building block in the synthesis of acrylic and methacrylic polymers used in paints, coatings, and surface finishes, where it contributes to film formation, durability, and weatherability.
- Textile Treatments: It is used in textile treatments and finishes to impart water repellency, stain resistance, and wrinkle resistance to fabrics and garments, particularly in applications such as outdoor apparel and upholstery.
- Paper Coatings: Methyl acrylate-based polymers are utilized in paper coatings and treatments to enhance surface properties, printability, and resistance to moisture, grease, and chemicals in packaging and printing applications.
- Emulsions: It is employed in the production of acrylic emulsions used as binders, thickeners, and modifiers in various applications, including adhesives, paints, textiles, and paper coatings.
- Plastic Additives: Methyl acrylate-based copolymers are used as additives in plastic formulations to improve impact resistance, flexibility, and processability of polymers, including polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), and polystyrene (PS).
- Chemical Intermediates: It serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of various specialty chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and personal care products, where it undergoes further chemical transformations to produce target molecules.
- Water Treatment: Methyl acrylate-based polymers are used in water treatment processes, such as flocculation, coagulation, and sedimentation, to remove impurities, suspended solids, and contaminants from wastewater and drinking water supplies.
- Emulsion Polymerization: It is used as a reactive monomer in emulsion polymerization processes to produce latex dispersions and emulsions used in paints, coatings, adhesives, and textile treatments.
- Resin Modifiers: Methyl acrylate-based polymers are used as modifiers and additives in resin formulations to improve flexibility, adhesion, and impact resistance in applications such as fiberglass composites, automotive coatings, and industrial coatings.
- Personal Care Products: It is employed in the production of personal care products, such as hair styling gels, nail polishes, and cosmetics, as a film-forming agent, binder, and fixative for active ingredients.