Methacrylic Acid

Product Description
Methacrylic acid (MAA) is a functional monomer with various industrial and commercial applications.
Product:
Methacrylic Acid
CAS:
79-41-4
Synonym:
MAA; 2-Methacrylic acid; 2-Methylpropenoic acid
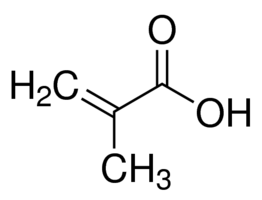
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Colorless viscous liquid
Boiling point
163 °C
Density
1.015 g/cm3
Melting point
12 - 16 °C
Molecular Weight
86.09
Odor
Acrid unpleasant odor
Purity
99 %
Refractive index
1.431
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Methacrylic Acid
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Methacrylic Acid used in many
industry applications
Methacrylic acid is a chemical compound with various industrial and commercial applications. Here's a list of some of its uses:
- Polymers and Plastics: Methacrylic acid is a key monomer in the production of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass. PMMA is used in a wide range of applications, including transparent panels, optical lenses, signs, displays, and medical devices. It offers excellent optical clarity, weather resistance, and impact strength, making it a versatile alternative to glass in many applications.
- Coatings and Paints: Methacrylic acid and its esters are used as monomers in the production of acrylic-based coatings, paints, and sealants. Acrylic coatings offer fast drying, good adhesion, and excellent weatherability, making them suitable for architectural coatings, automotive finishes, industrial coatings, and marine coatings.
- Adhesives and Sealants: Methacrylic acid-based polymers are used as adhesives and sealants in construction, automotive, and industrial applications. These polymers provide strong bonding strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making them suitable for bonding a wide range of substrates, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
- Medical Devices: Methacrylic acid and its derivatives are used in the production of medical devices and implants, such as bone cements, dental materials, and intraocular lenses. Acrylic-based materials offer biocompatibility, sterilizability, and ease of processing, making them suitable for various medical applications.
- Textile Auxiliaries: Methacrylic acid is used in textile finishing processes as a polymerizable monomer or as a precursor to functional polymers. Acrylic-based coatings and finishes provide wrinkle resistance, crease recovery, and stain resistance to fabrics and garments, enhancing their performance and durability.
- Water Treatment: Methacrylic acid-based polymers are used in water treatment processes as flocculants, coagulants, and scale inhibitors. These polymers help remove suspended solids, organic matter, and metal ions from water and wastewater, improving water quality and reducing environmental pollution.
- Printing and Inks: Methacrylic acid and its esters are used as components in printing inks and toners for offset printing, screen printing, and digital printing applications. Acrylic-based inks offer fast drying, vibrant colors, and good adhesion to various substrates, making them suitable for packaging, labels, and graphic arts.
- Electronics: Methacrylic acid-based polymers are used in electronic applications as encapsulants, adhesives, and coatings for electronic components and circuit boards. Acrylic-based materials offer good electrical insulation, thermal stability, and moisture resistance, protecting electronic devices from environmental hazards.
- Personal Care Products: Methacrylic acid and its esters are used in the formulation of personal care products, such as nail polishes, hair styling gels, and denture adhesives. Acrylic-based polymers provide film-forming properties, adhesion, and durability in cosmetic formulations.
- Adhesive Tapes: Methacrylic acid-based adhesives are used in pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes for bonding and sealing applications. These adhesives offer good tack, peel strength, and shear resistance, providing reliable bonding performance in packaging, automotive, and medical tape applications.