Coconut Oil

Product Description
Coconut oil, derived from the kernel or meat of mature coconuts, is a versatile natural product with numerous industrial applications.
Product:
Coconut Oil
CAS:
8001-31-8
Synonym:
Coconut fat; Cocos Nucifera Oil; Copra oil
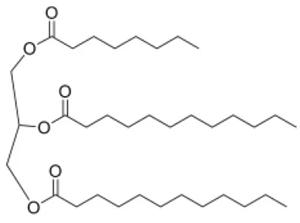
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
Off-white to yellow oily solid or liquid
Boiling point
>232 °C
Density
0.903 g/cm3
Flash Point
113 °C
Melting point
21-25 °C
Odor
Slight coconut odor
Purity
99%
Refractive index
1.445
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote



Coconut Oil used in many
industry applications
Coconut oil, derived from the kernel or meat of mature coconuts, is a versatile natural product with numerous industrial applications. Here are some of its key industrial uses:
- Food Industry: Coconut oil is widely used in the food industry for cooking, frying, baking, and flavoring. It is a popular choice for its high smoke point, mild flavor, and ability to impart a pleasant aroma to various dishes. Coconut oil is also used in the production of margarine, confectionery, and snack foods.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: It is a common ingredient in cosmetics, skincare products, and haircare formulations due to its moisturizing and emollient properties. Coconut oil is used in lotions, creams, soaps, shampoos, conditioners, and lip balms to hydrate, soften, and protect the skin and hair.
- Pharmaceuticals: Coconut oil is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations and medicinal products for its potential health benefits. It is used as a base or carrier oil in topical ointments, creams, and lotions for skin conditions such as eczema and dermatitis. Coconut oil is also consumed orally as a dietary supplement for its purported antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
- Industrial Lubricants: Due to its high stability, viscosity, and lubricating properties, coconut oil is used as a lubricant in various industrial applications. It is employed as a natural alternative to mineral oil-based lubricants in machinery, equipment, and hydraulic systems, particularly in environments where biodegradability and eco-friendliness are desired.
- Bioplastics and Polymers: Coconut oil can be processed into biodegradable plastics and polymers, offering a renewable and sustainable alternative to conventional petroleum-based plastics. Bioplastics derived from coconut oil are used in packaging materials, disposable utensils, and agricultural films, reducing the environmental impact of plastic waste.
- Biofuels: Coconut oil is a source of biodiesel, a renewable alternative to fossil fuels for transportation and energy generation. Biodiesel produced from coconut oil can be blended with diesel fuel or used as a standalone fuel in diesel engines, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on non-renewable resources.
- Soap and Detergents: Coconut oil is a key ingredient in the production of soaps, detergents, and household cleaning products. It provides cleansing, foaming, and moisturizing properties to bar soaps, liquid soaps, laundry detergents, and dishwashing liquids, making them effective for removing dirt, grease, and stains.
- Textile Industry: Coconut oil is used in the textile industry for fabric softening and conditioning. It is applied to textiles during processing to improve softness, smoothness, and flexibility, enhancing the comfort and feel of clothing, linens, and other textile products.
- Animal Feed and Agriculture: Coconut oil and its by-products are used in animal feed formulations as a source of energy and nutrition for livestock, poultry, and aquaculture. Coconut oil cake, a by-product of oil extraction, is used as a protein-rich feed ingredient for livestock and as organic fertilizer in agriculture.
- Wood Preservation: Coconut oil is sometimes used as a natural wood preservative and finish for furniture, flooring, and outdoor structures. It penetrates the wood fibers, nourishes the wood, and provides protection against moisture, insects, and fungal decay, extending the lifespan of wooden materials.