Tetrahydrophthalic Anhydride

Product Description
Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, also known as hexahydrophthalic anhydride, is a cyclic dicarboxylic anhydride with various industrial applications.
Product:
Tetrahydrophthalic Anhydride
CAS:
85-43-8
Synonym:
Hexahydrophthalic anhydride; 1,2,3,6-Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride
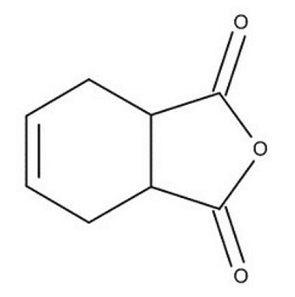
Structure:
Typical Characteristics
Appearance
White crystalline powder
Boiling point
195°C/5 mmHg
Density
1.36 g/cm3
Flash Point
157 °C
Melting point
102 °C
Molecular Weight
152.15
Purity
99%
Refractive index
1.4810
Uses, Applications & Markets
Key applications
get a quote
We Offer Tetrahydrophthalic Anhydride
in various grades
A few of the grades available are listed below:



Tetrahydrophthalic Anhydride used in many
industry applications
Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, also known as hexahydrophthalic anhydride, is a cyclic dicarboxylic anhydride with various industrial applications. Here are some of its main uses:
- Epoxy Resins: Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride is a key raw material in the production of epoxy resins. It is commonly used as a hardener or curing agent for epoxy formulations, where it reacts with epoxy groups to form crosslinked networks. This results in the production of epoxy adhesives, coatings, and composites with enhanced mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and heat stability.
- Plasticizers: It is utilized as a plasticizer in polymer formulations to improve flexibility, softness, and processability of plastics and elastomers. Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride can reduce the glass transition temperature of polymers, leading to increased flexibility and reduced brittleness. It is particularly used in the production of flexible PVC products, such as cables, flooring, and automotive parts.
- Polyester Resins: It serves as a crosslinking agent in the production of unsaturated polyester resins (UPR). Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride reacts with unsaturated monomers, such as styrene, to form thermosetting polyester networks. These polyester resins are widely used in the fabrication of fiberglass-reinforced plastics (FRP), automotive parts, marine coatings, and construction materials.
- Adhesive Formulation: Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride is used in the formulation of structural adhesives and sealants for bonding a wide range of substrates, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. It serves as a curing agent or crosslinker in epoxy and polyurethane adhesives, providing strong and durable bonds with excellent adhesion and chemical resistance.
- Paints and Coatings: It is incorporated into coatings and paints as a crosslinking agent or reactive diluent to enhance the performance and durability of the coating system. Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride can improve adhesion, hardness, and chemical resistance of coatings, providing long-term protection against corrosion, abrasion, and weathering.
- Textile Auxiliaries: It finds applications in the textile industry as a dye fixing agent and flame retardant. Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride can improve the color fastness and wash resistance of dyed fabrics by forming stable complexes with dyes. Additionally, it imparts flame retardant properties to textiles, reducing their flammability and enhancing safety.
- Surfactants: Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride derivatives are used as surfactants and emulsifiers in various industrial applications, including detergents, cleaners, and personal care products. They can reduce surface tension, improve wetting and spreading properties, and stabilize emulsions, leading to enhanced performance and efficacy of formulated products.
- Pharmaceutical Intermediates: It serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds, including drugs, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride derivatives can undergo various chemical reactions to produce functionalized compounds with specific pharmacological activities and functionalities.
- Textile Sizing: It is used in textile sizing formulations as a binder or film-forming agent to improve the strength and dimensional stability of yarns and fabrics. Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride can form crosslinked networks with fibers, enhancing their resistance to mechanical stress and abrasion during weaving and processing.
- Food Packaging: Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride derivatives are used in the production of food packaging materials, such as coatings and films. They can provide barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and other contaminants, extending the shelf life and freshness of packaged food products.